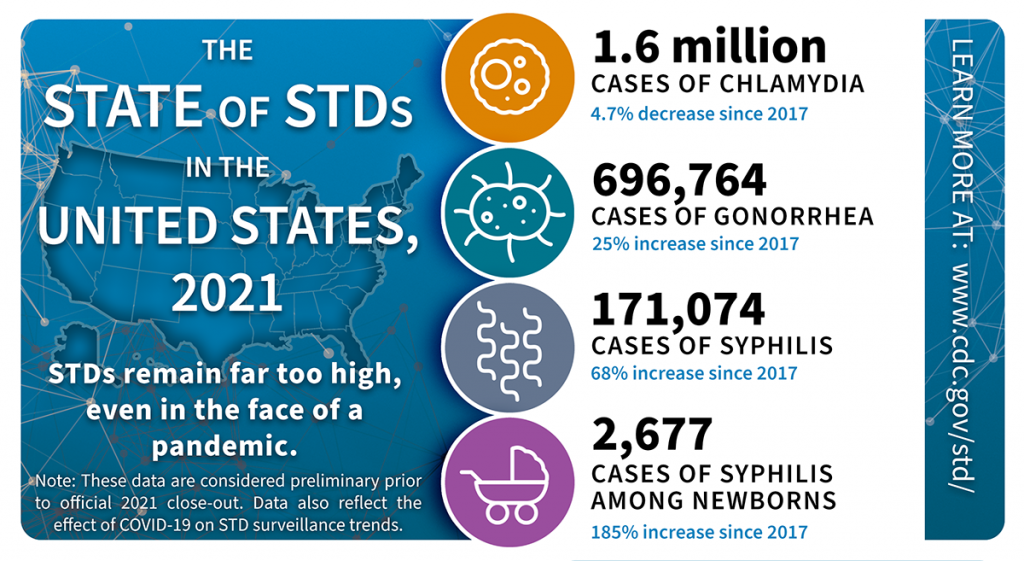
Photo courtesy of CDC, Caption: The rate of STDs have been going up for the past few years. Though not always fatal, they can be easily spread.
Most common STDs’ symptoms and causes
Read Time2 Minute, 7 Second
- Herpes: Spreads through contact with infected areas – usually through sex or kissing – and can cause: itching, pain, sores, ulcers, and scabs. It lays dormant in the body with occasional outbreaks typically in the genital or mouth area. Flare-ups can be caused by sunlight, irritation, menstruation, and stress. There is no cure but antiviral medication can reduce outbreaks and chances of transmission.
- HPVs: Causes warts on genitals or surrounding skin, but can appear elsewhere depending on the strain. It transmits via sexual contact. There is a vaccine available to prevent certain strains of HPV, but the warts may be treated via removal.
- Syphilis: A bacterial infection that is spread via sexual contact. Those infected will go through three stages with varying symptoms and intensity. The first stage is from the 3-90 day mark, where sores will appear. The second is the 4-10 week mark, where a full body rash will develop. No symptoms appear until the last stage, the 3-15 years mark, where internal damage may occur to the heart, lungs, eyes, or brain. A shot of penicillin can be used to cure the early stages – antibiotics is another option.
- Hepatitis B: Spreads via bodily fluids and does damage to the liver, though it can be prevented by vaccination. Symptoms include yellowness in the eyes, dark urine, or abdominal pain.
- Hepatitis C: Transfers through blood-to-blood contact and causes inflammation in the liver. Though most experience no symptoms, there can be yellowness of the eyes, lack of appetite, and fatigue. Hep C can be treated using antiviral medications, but unlike Hep B, there is no vaccine for it.,
- Gonorrhea: A sexually transmitted bacterial infection that may cause painful urination, abnormal discharge, pain in the lower abdomen for women, or pain in the genitals for men. Symptoms may not appear, but in the worst cases, it can cause infertility. Gonorrhea can be treated with antibiotics.
- Chlamydia: A bacterial infection that may be transmitted sexually and is most common in young women. Some cases have no symptoms, but they may include: genital pain and vaginal discharge. In women, it can lead to permanent damage to the reproductive system and a fatal ectopic pregnancy. Antibiotics may be used as a treatment.
- AIDs: Caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that can spread through blood or genital fluids,. HIV may cause interference with the body’s ability to fight off diseases and viruses, though not all develop AIDs from HIV. Various medications are available to control the virus and slow the disease progression.